Missing HCC Codes Leave Money on the Table

Improper clinical documentation of one patient can mean a difference of more than $10,000 in yearly estimated health care costs. How much money are you potentially leaving on the table?
Medicare/Medicaid and other insurance companies use Hierarchical Condition Categories (HCC) coding, a risk-adjustment (RA) model, to assign patients a Risk Adjustment Factor (RAF) score. They use this score to predict future health care costs and reimbursements associated with each patient on an annual basis.
As a clinician, you tell your patient’s health story through medical coding and documentation. When done correctly, this not only provides the patient with better overall care, but also improves your practice’s profitability.
Know Your RAF Score
HCC assigns risks scores to each patient using ICD-10-CM diagnosis coding. There are 9,500 ICD-10-CM codes that map to 86 total HCC codes within 19 different HCC categories. The diagnosis gets an HCC score, and the patient receives a RAF score made up of HCC scores.
Insurance companies expect patients with few serious health conditions to have average medical costs for a given time. A risk score of 1.000 is an average patient, and Medicare would expect to spend $10,000 on that patient. For patients with a RAF score of 1.100, Medicare would expect to spend $11,000 ($10,000 x 1.100). They expect patients with chronic conditions have a higher RAF score and higher health care utilization and associated costs.
HCC Coding and RAF Score Process:
- Clinicians treat patient on RA model
- Clinicians document code diagnoses correctly
- HCC and RAF scores are determined by accurate code assignment based on clinician documentation
- Reimbursement levels are set based on HCC and RAF scores
HCC Impact on Cinicians
Documentation is an ongoing process. The risk adjustment calendar restarts each year in January, and insurance companies consider all patients healthy until clinicians once again add active diagnosis into the documentation. Chronic conditions and comorbidities affect RAF scores and, therefore, reimbursement levels. That’s why it’s important to collaborate with any other clinicians or specialists a patient sees. Failing to document chronic conditions affect everyone’s reimbursement.
Payment Differences Based on HCC Coding
Poor coding quality creates inaccuracies and the potential loss of revenue for clinicians, not to mention misallocated resources and missed opportunities for patient care. An article on HCC coding and risk adjustment from AAFP’s Family Practice Management Journal states, “Failing to adequately capture a patient’s risk through documentation and coding may lead to an inaccurately low level of attributed risk and eventually to reduced reimbursement. On the other hand, accurate and thorough documentation and coding will give your practice its best chance of earning shared savings and in turn help you become more successful in managing your patient population.”
IKS Health Finds Missing Codes
Are your RAF scores much lower or higher than the national average of 1.00? This could indicate either missing HCCs or possible over coding. IKS Medical Coding Solutions assigns ICD-10-CM diagnosis codes and provides documentation review and recommendations for improvement or missed coding opportunities.
We also provide Medical Coding Audits to show gaps in documentation and any inaccurate code assignments. More specific coding results in a more accurate picture of your patients and the complexity of their conditions and treatment.
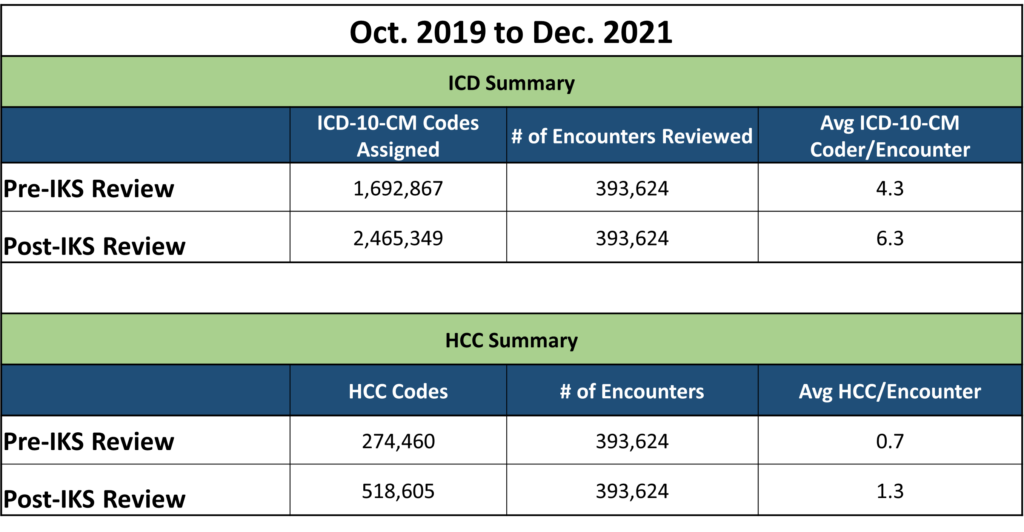
In a span of about two years, IKS found clients an additional 770,000+ ICD-10-CM codes and was able to assign more than 244,000 HCC codes. This brought the average HCC score from 0.7 to 1.3.
Our clients receive specific clinician findings and recommendations for coder and/or physician education to better improve the process going forward. Find your missing codes, improve your patient care, and stop leaving money on the table with IKS Medical Coding Solutions.


